What can be done for the condition?
Physician’s Review
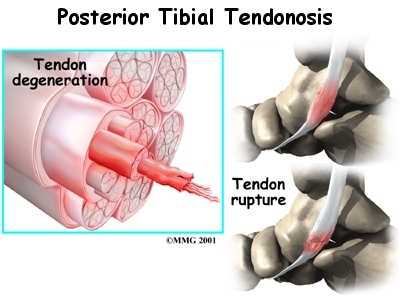
Your doctor may prescribe anti-inflammatory medications, such as ibuprofen or aspirin if you are in the stage of injury where inflammation is a culprit.
A cortisone injection, sometimes used to ease inflammation in other types of injuries, is usually not appropriate for this condition, since the tendon is more likely to rupture following injection. Some physicians recommend a slightly different cortisone treatment, other than injection, called iontophoresis. Iontophoresis is a treatment that uses electric current to deliver cortisone medicine through the skin to the inflamed tendon. The risk of tendon rupture is much less when this method is used.
Nonsurgical Rehabilitation
Physiotherapy at Next Step Physio is extremely beneficial in treating posterior tibial problems.
During your first few treatments at Next Step Physio your physiotherapist will focus on relieving your pain. They may use ice, heat, ultrasound, or other electrical modalities on the instep of your foot or up the medial shin to provide you with relief. Icing or heating these areas at home will provide similar relief. Your therapist may also massage the bottom of your foot, calf, and muscles around your shin. Massage can be particularly useful in relieving your discomfort. Unfortunately these types of treatments only provide temporary relief; addressing the real problem of why the posterior tibial tendon is being stressed will provide more long-term relief to your injury and help to avoid an irritated tendon from developing into a chronic problem, or from rupturing.
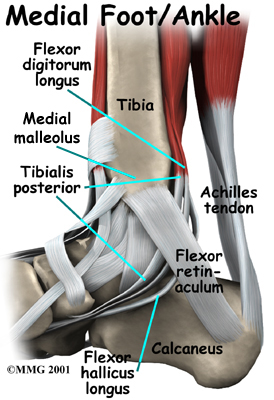
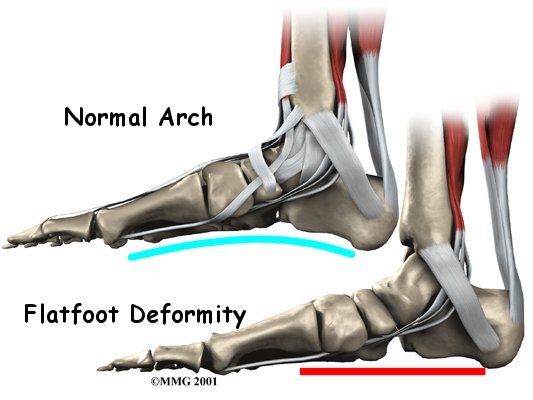
Physiotherapy exercises will begin with strengthening exercises for the small muscles of your foot and posterior tibialis muscle. As mentioned above, these muscles work to lift and support the arch of the foot, along with the muscles of the hip, which control alignment down the lower leg chain, and also assist in lifting the arch of the foot. A Theraband may be used to provide added resistance to the muscles of the foot, and to strengthen the hip muscles. Your therapist will also prescribe stretching exercises, particularly for the muscles of your calf, which, when tight, can force the foot out of alignment. When performing all stretches it is imperative that you maintain proper alignment of your foot and arch so as not to compound the forces going through an already irritated posterior tibial tendon. Your physiotherapist will give you feedback on whether or not your alignment during your exercises is sufficient.
Being that posterior tibial tendon problems tend to develop over time, it is common for patients to not even notice that their feet may be flat or their alignment is off. The position of your feet becomes the ‘new normal.’ Re-learning the proper position of your arch is crucial to relieving the pain in your posterior tibial tendon as well as stopping the progression of the tendon problem and preventing a resultant deformity developing in the foot. Proprioception is the term used to describe one’s sense of joint position. Your physiotherapist will teach you what the correct position of your foot and arch should be and will give you exercises that challenge the proprioception of your knee, foot, ankle, and arch. Initially these exercises may be while you are simply sitting but as you progress, your physiotherapist will advance your exercises so you are doing them in standing, and eventually just on one foot at a time. The standing position is an important position to work up to as it is much more functional in mimicking normal everyday activities such as walking or stair climbing. Eventually your physiotherapist will prescribe exercises that are extremely challenging, especially if you are involved in a high-level sport. Exercises such as squatting and jumping will be added and you will be required to do these activities while maintaining proper foot, arch and leg alignment.
If you have not already invested in some orthotics to assist with supporting your arch and taking some pressure off of your posterior tibial tendon your physiotherapist will advise you on whether you should purchase some, and where to do this. Often taping the bottom of the foot, which your physiotherapist can do, and can teach you to do on your own, can be trialed before expensive orthotics are purchased. Taping may be enough in mild cases of posterior tibial tendon pain, as long as you can learn to control the position of your foot and maintain this position during high-level activities. In most cases shoe inserts, even pre-fabricated ones, will significantly improve the symptoms of a posterior tibial tendon problem, and will be recommended to both relief symptoms and to avoid any progression of the injury. Custom fit orthotics are recommended for any individuals who have a significant flattened arch, or for whom prefabricated ones do not relieve their symptoms.
As mentioned above, excess weight can be the cause of posterior tibial tendon problems. Losing excess weight can greatly improve the pain you feel in your foot and make it easier to maintain normal foot alignment during everyday activities. Your physiotherapist at Next Step Physio can discuss weight loss strategies with you and if need be, refer you to a Nutritionist who can also assist with this goal. Often it is difficult to exercise and increase your energy expenditure to lose weight when you have a painful foot, however, there are several safe activity options that your therapist can discuss with you, such as stationary cycling or swimming.
Activity modification is an important part of our treatment for posterior tibial problems at Next Step Physio. Your physiotherapist will strongly advise you to avoid any activities that cause you discomfort while you still have symptoms. This may also mean resting for a short period from any sport you do, or at least decreasing your amount of activity over a period of time. Your physiotherapist will specifically guide you regarding the needed rest for your individual injury. This rest may seem quite difficult to achieve, however it is well known that without a relative rest for a painful foot, there is little chance for it to heal. A period of rest where the foot is not being aggravated also greatly improves the ability of any medication you may be taking, along with the physiotherapy treatment you are receiving, to assist the healing of the injury. Your physiotherapist will advise you when it is safe to slowly start back at your activity after your period of rest.
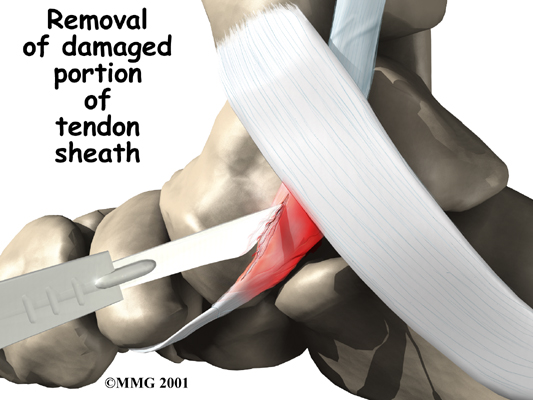
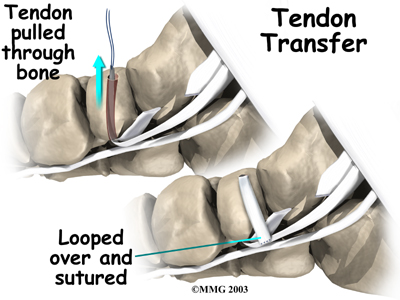
Unfortunately, not all posterior tibial tendon problems will respond to the physiotherapy treatment we provide at Next Step Physio. If your symptoms persist or it appears that your foot is not responding to the treatment the way that your physiotherapist would expect it to your physiotherapist will refer you on to your family physician or an Orthopaedic Surgeon to discuss a more aggressive form of treatment.
Next Step Physio provides services for physiotherapy in Edmonton.